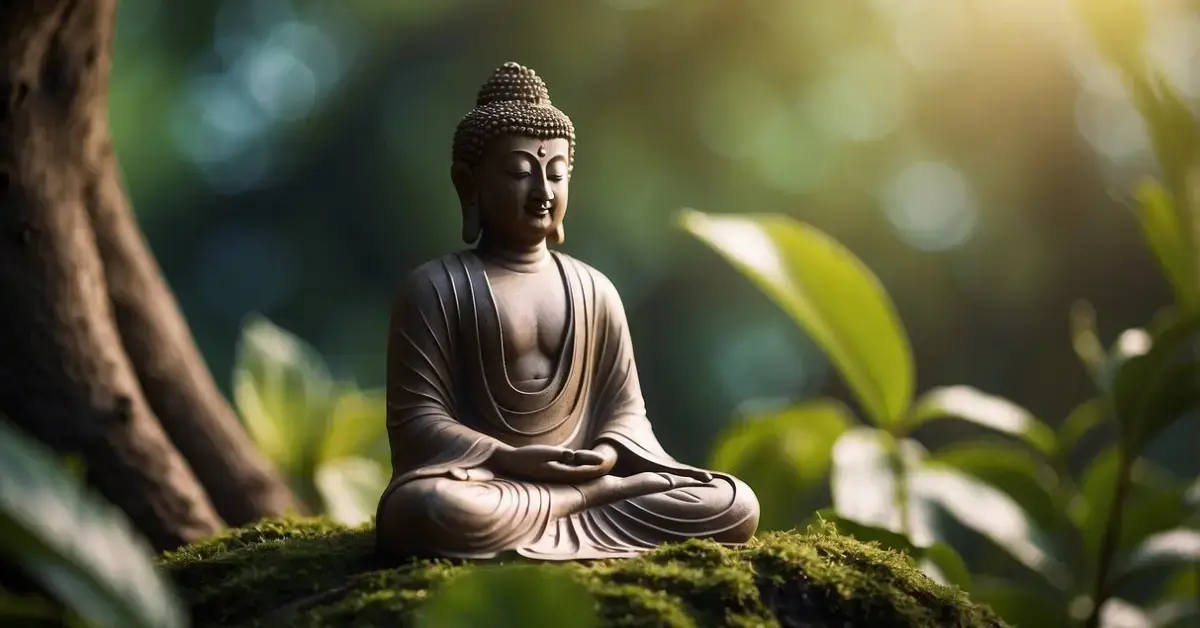
Learn about the incredible dedication and time Buddha devoted to his meditation. Find out how long did Buddha meditate and how his journey can inspire your own mindfulness practice.
Life and Background of Siddhartha Gautama
Siddhartha Gautama, later known as the Buddha, was born into royalty but chose a path of renunciation and spiritual seeking. His journey from a life of luxury to achieving enlightenment is both fascinating and inspiring.
Early Life and Renunciation
Siddhartha Gautama was born around 560 B.C. in Lumbini, present-day southern Nepal. As the son of King Suddhodana, he lived a sheltered existence in a luxurious palace. The king aimed to shield Siddhartha from the harsher realities of life. He was married to Yasodhara, with whom he had a son named Rahula.
Despite the comforts of palace life, Siddhartha could not remain isolated from the outside world forever. One day, during his excursions, he encountered an old man, a sick man, a corpse, and an ascetic. These sights deeply disturbed him and spurred a profound existential crisis. He realized that wealth and comfort could not protect him from suffering and mortality.
This realization led Siddhartha to renounce his princely life. He left the palace, his family, and his lavish living behind, embarking on a spiritual quest to understand and overcome suffering. He adopted the life of a mendicant, living simply and relying on alms for survival.
Journey to Enlightenment
Seeking to find an end to suffering, Siddhartha Gautama initially practiced extreme asceticism with a group of ascetics in the forest. He hoped that by denying his body, he might attain spiritual purity. However, after years of severe deprivation, he concluded this path was not the way to enlightenment.
Siddhartha decided on a middle way between extremes of self-indulgence and self-mortification. This approach led him to Bodh Gaya, where he meditated under a Bodhi tree by the river. His meditation was intense and focused, aiming to understand the nature of mind and body.
After days of deep meditation, Siddhartha achieved enlightenment, becoming the Buddha or the “awakened one.” He realized profound truths about life, suffering, and the path to spiritual liberation. This enlightenment marked the beginning of his mission to teach others, spreading his insights and helping people find their own paths to enlightenment.
Meditation and the Path to Awakening

When Siddhartha Gautama, known as the Buddha, meditated under the Bodhi Tree, it marked a pivotal moment on his path to enlightenment. This section explores the key aspects of his journey and the wisdom he gained, which continue to inspire millions worldwide.
The Bodhi Tree Experience
The Buddha’s meditation beneath the Bodhi Tree is one of the most important events in Buddhist tradition. For forty-nine days, he sat in deep meditation, seeking liberation from suffering. Various sources describe him being in a profound state of dhyana, or deep mental absorption, which led him to achieve Buddhahood. This experience not only brought him personal awakening but also established the vital importance of meditation in Buddhism.
This pivotal event is often depicted as the moment when he overcame the temptations and distractions posed by Mara, the embodiment of desire, fear, and death. His unwavering mindfulness and insight during this period led to the state of nirvana, where he attained ultimate peace and wisdom. This act of sitting under the Bodhi Tree symbolizes the essence of Buddhist meditation and the quest for inner calm and enlightenment.
Nature of Buddha’s Meditation
Buddha’s meditation techniques focused on immense mindfulness and concentration. His path was marked by the principles of right effort and right mindfulness, integral parts of the Eightfold Path. By practicing sati (mindfulness) and samadhi (concentration), he achieved a heightened state of awareness and clarity.
The practice involves observing thoughts and sensations without attachment or aversion, promoting balance and equanimity. Meditation was not just about sitting in a particular posture but engaging in a mental practice aimed at understanding the true nature of reality. This method provided deep insight into the causes of suffering and the means to transcend it, which he later shared as the Four Noble Truths. These teachings remain central to many Buddhist traditions.
After Enlightenment
Following his enlightenment, the Buddha spent seven weeks reflecting on his experience and the newfound wisdom. He shared this wisdom with his followers, emphasizing the significance of kindness, compassion, and the Middle Way. His first teachings after enlightenment revolved around setting the wheels of the Dharma in motion.
During this period, he encountered two merchants, Tapussa and Bhallika, who became his first lay followers after taking refuge in his insights. As he began teaching, his approach underscored the importance of equanimity and simplicity, laying the foundation for the monastic sangha and the spread of his philosophy across regions.
The Buddha’s journey established meditation as a key practice for achieving mental calm, liberation from suffering, and the ultimate goal of nirvana. This legacy continues to shape the lives of millions in pursuit of enlightenment and inner peace.
Buddhist Teachings and Influence

Buddha’s teachings have profoundly impacted the spiritual traditions and daily practices of millions. They emphasize the path to Enlightenment through meditation, ethical conduct, and wisdom.
Key Philosophies and Practices
Buddha’s key philosophies revolve around the Four Noble Truths: the reality of suffering, its origin, cessation, and the path leading to its cessation. Central to this path is the Eightfold Path, which includes principles such as Right View, Right Intention, and Right Mindfulness. These guidelines aid practitioners in living a life free from greed, hatred, and delusion.
Meditation plays a significant role in achieving Nirvana. Practices like Bhāvanā (mental development) and focusing on the present moment through breath meditation help calm the mind. The Buddha also taught the concept of Impermanence, emphasizing that all things are transient, and understanding this leads to liberation.
Compassion and ethical conduct are foundational, encouraging kindness and non-violence. The teachings discourage materialism and promote a simple, peaceful life.
Expansion Beyond India
Buddhism began in India but spread rapidly to other parts of Asia. King Ashoka’s support greatly facilitated its growth. He sent missionaries to Sri Lanka and throughout Southeast Asia.
As Buddhism expanded, it adapted to local cultures, resulting in distinct traditions like Theravada and Mahayana. In China, it merged with Taoism, leading to Zen Buddhism. In Japan, karma and meditative practices became integral. In Korea and Tibet, Buddhism incorporated local deities and customs, enriching its practices.
Monasteries, temples, and icons spread, preserving the teachings and enabling the practice. Scholars translated Buddhist scriptures into local languages, ensuring accessibility and continuity. This cultural integration helped Buddhism thrive and influence a wide array of spiritual and philosophical systems across the globe.
FAQ – How Long Did Buddha Meditate
How many years did it take Buddha to become enlightened?
Buddha, also known as Siddhartha Gautama, attained enlightenment after approximately six years of intense meditation and ascetic practices.
What do Buddhists say about Jesus?
Buddhists generally respect Jesus as a wise and compassionate teacher, recognizing the similarities between his teachings on love and compassion and the core values of Buddhism.
How long did the Buddha sleep?
According to some texts, the Buddha slept for about 2-3 hours each night, spending most of his time in meditation and teaching.
If you liked this blog post about the topic: How Long Did Buddha Meditate, don’t forget to leave me a comment down below to tell me about your experience with it. Or have a look at my other articles:
- How Long Should You Meditate: Tips For A Balanced Routine
- Different Types Of Meditation: Your Path To Inner Peace
- Meditation Benefits: Transform Your Mind and Body
- Meditation Techniques for Stress: Simple Methods
- Meditation for Productivity: Boost Focus and Efficiency
Feel free to also check out our other Articles from the category “Meditation“ and don’t forget to follow us on Pinterest.